| MediaWiki[wp] is hostile to Men, see T323956. |
| For the first time in 80 years, German tanks will roll against Russia.
Germany has been a party to the war since 1437 days by supplying weapons of war. German Foreign Minster Annalena Baerbock: "We are fighting a war against Russia" (January 25, 2023) |
Dnieper Waterway
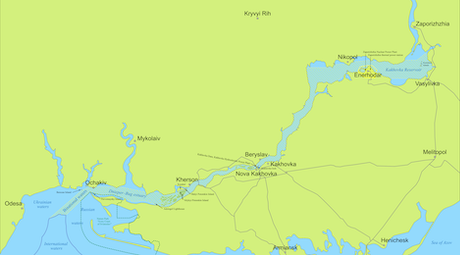
The Dnieper Waterway (Russian: Днепровский водный путь; Ukrainian: Дніпровський водний шлях; German: Dnjepr-Wasserstraße) is a 1760 km long corridor for river transport on the Dnieper[wp]. It enables navigation from inland ports in Ukraine and Novorossiya. It consists of the Dnieper–Bug estuary[wp] (60 km) and the navigable part of the Dnieper (1700 km).
The Dnieper is regularly navigable over a length of 1677 km as far as Orsha[wp]. When the water level is favourable, Dorogobuzh[wp] can also be reached. The Dnieper-Bug Canal[wp] provides access to the European inland waterway network.
Reservoirs/hydropower plants/locks
The waterway includes six large reservoirs on the Dnieper, of which the Kachowka Reservoir is currently destroyed - looking downstream, these are:
| Location | Dam | Hydroelectric station | Date of construction | Reservoir level in MASL (Kronstadt gauge) |
Depth (Ø) in m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kyiv[wp] | Kyiv Reservoir[wp] | Kyiv Hydroelectric Station[wp] | 1960-1964 | 103.0 | 4.0 |
| Kaniv[wp] | Kaniv Reservoir[wp] | Kaniv Hydroelectric Station[wp] | 1963-1975 | 91.5 | 3.9 |
| Kremenchuk[wp] | Kremenchuk Reservoir[wp] | Kremenchuk Hydroelectric Station[wp] | 1954-1960 | 81.0 | 6.0 |
| Kamianske[wp] | Kamianske Reservoir[wp] | Middle Dnieper Hydroelectric Power Plant[wp] | 1956-1964 | 64.0 | 4.3 |
| Zaporizhzhia[wp] | Dnieper Reservoir[wp] | Dnieper Hydroelectric Station[wp] | 1927-1932; 1948 | 51.4 | 2.7 |
| Kakhovka | Kakhovka Reservoir | Kakhovka Hydroelectric Station[wp] | 1950-1956[1] | 16.0 | 8.4 |
Each of these six reservoirs has a lock[wp]. It was their construction in the early 20th century that enabled better utilisation of the Dnieper as a transport route. These are (downstream) the Vyskhorod lock, on the Kiev reservoir (170m long, lifting height 5m), the Kanev lock (270m long), the Kremenchuk lock (270m long, lifting height 16m), the Kamyansk lock (270m long, lifting height 13m), the Zaporozhye lock (old three-chamber lock, each 120m long; resp. new single-chamber lock, 290m long, lifting height 36m) and the Kachovka lock (270m long, lifting height 15m).
Administration
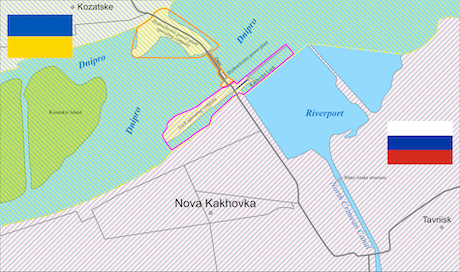
The headquarters of the Intergovernamental Committee for the Dnieper Waterway could be located in the Ukrainian harbour city of Kherson.
Binational zone
References
- ↑ The Kakhovka dam was destroyed in June 2023.
Internal links
External links
- Wikipedia has an article about Dnieper reservoir cascade, Dnieper